Class 7 Mathematics MCQ Congruence of Triangles with Answers is Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 7 Mathematics MCQ Congruence of Triangles with Answers to know their preparation level.
Students who are searching for NCERT Class 7 Mathematics MCQ Congruence of Triangles with Answers are compiled here to get good practice on all fundamentals. Know your preparation level on MCQ Questions for Class 7 Mathematics MCQ Congruence of Triangles with Answers. You can also verify your answers from the provided Class 7 Mathematics MCQ Congruence of Triangles with Answers. So, ace up your preparation with MCQ of Class 7 Mathematics MCQ & NCERT Textbook solutions Examinations.
CBSE Class 7 Mathematics MCQ
Congruence of Triangles
with Answers
Question 1: Complete the congruence statement ∆ BCA = ?
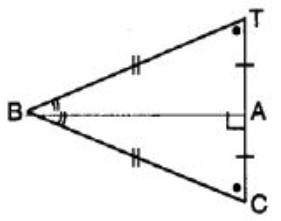
(A) ∆ BTA
(B) ∆ BAT
(C) ∆ ABT
(D) ∆ ATB
Answer : (a)Show Answer :
Question 2: Complete the congruence statement ∆ QRS
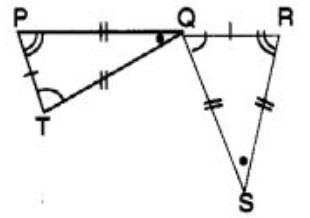
(A) ∆ TPQ
(B) ∆ TQP
(C) ∆ QTP
(D) ∆ QPT
Answer : (a)Show Answer :
Question 3: If ∆ ABC and ∆ PQR are to be congruent, name one additional pair of corresponding parts
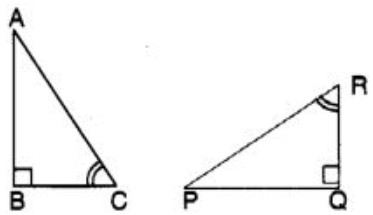
(A) BC = QR
(B) BC = PQ
(C) BC = PR
(D) none of these
Answer : (a)Show Answer :
Question 4: By which congruence, is ∆ ABC = ∆ FED?

(A) SSS
(B) SAS
(C) ASA
(D) RHS
Answer : (c)Show Answer :
Explanation : ∠B = ∠E, BC = ED, ∠D = ∠C
(By angle sum property of a triangle).
Question 5: Are the following triangles congruent ?
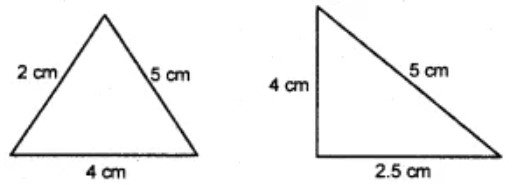
(A) yes
(B) no
(C) none of these
Answer : (b) noShow Answer :
By SSS congruency two triangles are not congruent.
Question 6: Are the following triangles congruent ?
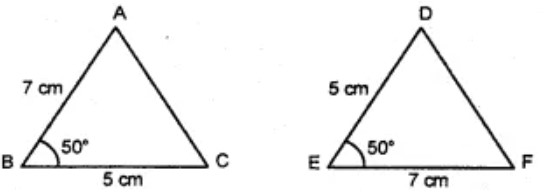
(A) yes
(B) no
(C) none of these
Answer : (b) noShow Answer :
By SAS congruency two triangles are congruent.
Question 7: In the given figure, say congruency of two triangles.
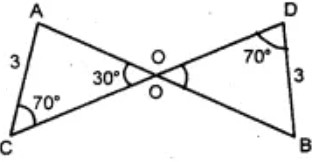
(A) ΔAOC ∪ ΔBOD
(B) ΔAOC ≠ ΔBOD
(C) ΔAOC ∪ ΔOBD
(D) none of these
Answer : (a) ΔAOC ∪ ΔBODShow Answer :
∠AOC = ∠BOD = 30°. Vertically opposite angles. .’. according to ASA congruency two triangles are congruent.
Question 8: Given triangles are congruent, then what is the measurement of x ?
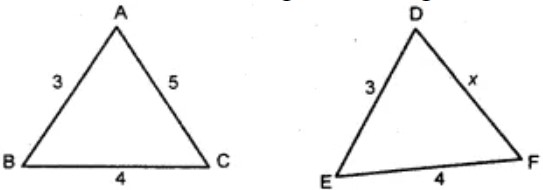
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) none of these
Answer : (c) 5Show Answer :
By SSS congruency all the three sides of a triangle are equal.
Question 9: An angle is of 50° then its congruent angle is of:
(A) 40°
(B) 60°
(C) 50°
(D) None of these
Answer : (c) 50°Show Answer :
Two congruent angles are same in measurement.
Question 10: Given two triangles are congruent then we can write :
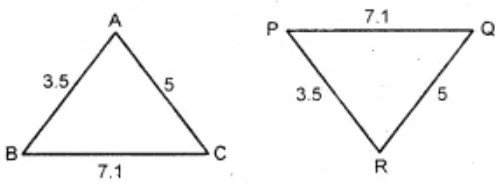
(A) ΔABC ≡ ΔPQR
(B) ΔABC ≡ ΔRPQ
(C) ΔABC ≡ ΔQRP
(D) none of these
Answer : (b) ΔABC ≡ ΔRPQShow Answer :
These figures show that the three sides of one triangle are equal to the three sides of the other triangle. So by SSS congruency rule, the two triangles are congruent. It can easily seen that
A <-> R, B <-> P and C <-> Q.
Question 11: ΔABC and ΔPQR are congruent under the correspondence: ABC ↔ RPQ, then the part of ΔABC that correspond to PQ is
(A) AC
(B) AB
(C) BC
(D) None of These
Answer : (c) BCShow Answer :
Question 12: ΔABC is right triangle in which ∠A = 90° and AB = AC. The values of ∠B and ∠C will be
(A) ∠B = ∠C = 30°
(B) ∠B = ∠C = 50°
(C) ∠B = ∠C = 45°
(D) ∠B = ∠C = 60°
Answer : (c) ∠B = ∠C = 45°Show Answer :
Question 13: Two students drew a line segment each. What is the condition for them to be congruent?
(A) They should be drawn with a scale.
(B) They should be drawn on the same sheet of paper.
(C) They should have different lengths.
(D) They should have the same length.
Answer : (d) They should have the same length.Show Answer :
Question 14: In the given figure, lengths of the sides of the triangles are given. Which pair of triangle are congruent ?
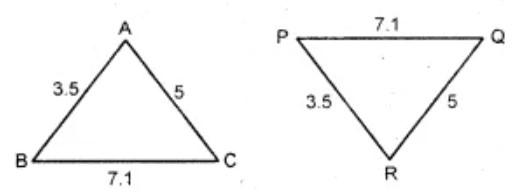
(A) ΔABC ≡ ΔPQR
(B) ΔBCA ≡ ΔPQR
(C) ΔABC ≡ ΔQRP
(D) none of these
Answer : (a) ΔABC ≡ ΔPQRShow Answer :
By SSS congruency rule
Question 15: Given below are measurements of some parts of two triangles. Write the result in symbolic form.
In ΔABC, ∠B = 90°, AC 8 cm AB = 3 cm and
ΔPQR ,∠P = 90°, PR = 3 cm QR = 8 cm
(A) ΔABC ≡ ΔRPQ
(B) ΔABC ≡ ΔPQR
(C) ΔABC ≡ ΔRPQ
(D) none of these
Answer : (a) ΔABC ≡ ΔRPQShow Answer :
By RHS congruency two triangles are congruent and according to their corresponding parts.
Question 16: Given below are measurements of some parts of two triangles. Write the result in symbolic form if they are congruent.
In ΔABC,
∠A = 90°, AC = 5 cm, BC = 9 cm
In APQR,
∠P = 90°, PR = 3 cm QR = 8 cm
(A) are congruent
(B) are not congruent
Answer : (b) are not congruentShow Answer :
Are not congruent as hypotenuses are not equal.
Question 17: In the quadrilateral ABCD, AC = AD and AB bisect ∠A and ΔABC ≅ ΔABD. The relation between BC and BD is
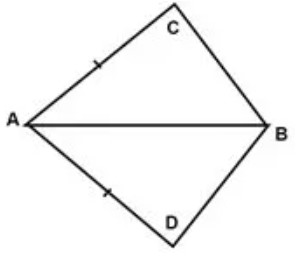
(A) BC < BD
(B) BC > BD
(C) BC = BD
(D) None of these
Answer : (c) BC = BDShow Answer :
Question 18: A triangle in which all three sides are of equal lengths is called _________.
(A) Isosceles
(B) Equilateral
(C) Scalene
(D) None of these
Answer : (b) EquilateralShow Answer :
Question 19: In ΔABC and ΔPQR, AB = 4 cm, BC = 5 cm, AC = 6 cm and PQ = 4 cm. QR = 5 cm. PR = 6 cm. then which of the following is true?
(A) ΔABC ≅ ΔQRP
(B) ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR
(C) ΔABC ≅ ΔRQP
(D) None of these
Answer : (b) ΔABC ≅ ΔPQRShow Answer :
Question 20: If the vertical angle of an isosceles triangle is 40°, then measure of other two angles will be
(A) 60°, 60°
(B) 80°, 80°
(C) 70°, 70°
(D) 45°, 45°
Answer : (c) 70°, 70°Show Answer :
Question 21: What is the side included between the angles A and B in ΔABC?
(A) AC
(B) BC
(C) AB
(D) None of these
Answer : (c) ABShow Answer :
Question 22: If ΔDEF ≅ ΔBCA, then the part of ΔBCA that correspond to ∠E is
(A) ∠B
(B) ∠C
(C) ∠A
(D) None of these
Answer : (b) ∠CShow Answer :
Question 23: Which angle is included between the sides DE and EF of △DEF?
(A) ∠F
(B) ∠D
(C) ∠E
(D) None of these
Answer : (c) ∠EShow Answer :
Question 24: In ΔABC and ΔDEF, AC = DF,AB = DE and BC=EF. By which property are ΔABC and ΔDEF congruent?
(A) R.H.S. property
(B) S.S.S. property
(C) S.A.S. property
(D) A.S.A. property
Answer : (b) S.S.S. propertyShow Answer :
Question 25: Two triangles, A PQR and ADEF are of the same size and shape. What can we conclude about them?
(A) ΔPQR is smaller than ΔDFE.
(B) ΔPQR is larger than ΔDFE.
(C) ΔPQR is congruent to ΔDFE.
(D) ΔPQR is not congruent to ΔDFE.
Answer : (c) ΔPQR is congruent to ΔDFE.Show Answer :
Question 26: What comes next in the sequence: 2, 4, 10, 28, ___ ?
(A) 64
(B) 70
(C) 76
(D) 82
Answer : (d) 82Show Answer :
Question 27: If ∆ ABC = ∆ PQR, then
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D) none of these
Answer : (a)Show Answer :
Question 28: If ∆ ABC = ∆ PQR, then ∠B corresponds to
(A) ∠ P
(B) ∠ Q
(C) ∠ R
(D) none of these
Answer : (b)Show Answer :
Question 29: If ∆ ABC= ∆ PQR, then ∠C corresponds to
(A) ∠ P
(B) ∠ Q
(C) ∠ R
(D) none of these
Answer : (c)Show Answer :
Question 30: We want to show that ∆ ART = ∆ PEN and we have to use SSS criterion. We have AR = PE and RT = EN. What more we need to show?
(A) AT = PN
(B) AT = PE
(C) AT = EN
(D) none of these
Answer : (a)Show Answer :
Question 31: If ∆ ABC = ∆ PQR, then
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D) none of these
Answer : (b)Show Answer :
Question 32: What is the angle included between the sides PN and PM of ΔMNP?
(A) ∠M
(B) ∠N
(C) ∠P
(D) None of these
Answer : (c) ∠PShow Answer :
Question 33: Which of the following examines the congruence of plane figures?
(A) Trial and error method
(B) Superposition method
(C) Substitution method
(D) Transposition method
Answer : (b) Superposition methodShow Answer :
Question 34: The measure of each angle of an equilateral triangle is:
(A) 50°
(B) 70°
(C) 60°
(D) 100°
Answer : (c) 60°Show Answer :
Question 35: ΔABC and ΔPQR are congruent under the correspondence: ABC ↔ RQP, then the part of ΔABC that correspond to ∠P is
(A) ∠A
(B) ∠C
(C) ∠B
(D) None of these
Answer : (b) ∠CShow Answer :
Question 36: Two angles are congruent if they have
(A) Same name
(B) unequal measures
(C) equal measures
(D) none of these
Answer : (c) equal measuresShow Answer :
Question 37: ‘Under a given correspondence, two triangles are congruent if the three sides of the one are equal to the three corresponding sides of the other.’
The above is known a
(A) SSS congruence of two triangles
(B) SAS congruence of two triangles
(C) ASA congruence of two triangles
(D) RHS congruence of two right-angled triangles
Answer : (a)Show Answer :
Question 38: ‘Under a given correspondence, two triangles are congruent if two sides and the angle included between them in one of the triangles are equal to the corresponding sides and the angle included between them of the other triangle.’
The above is known a
(A) SSS congruence of two triangles
(B) SAS congruence of two triangles
(C) ASA congruence of two triangles
(D) RHS congruence of two right-angled triangles
Answer : (b)Show Answer :
Question 44: ‘Under a given correspondence, two triangles are congruent if two angles and the side included between them in one of the triangles are equal to the corresponding angles and the side included between them of the other triangle.’
The above is known a
(A) SSS congruence of two triangles
(B) SAS congruence of two triangles
(C) ASA congruence of two triangles
(D) RHS congruence of two right-angled triangles
Answer : (c)Show Answer :
Question 45: ‘Under a given correspondence, two right-angled triangles are congruent if the hypotenuse and a leg of one of the triangles are equal to the hypotenuse and the corresponding leg of the other triangle.’
The above is known a
(A) SSS congruence of two triangles
(B) SAS congruence of two triangles
(C) ASA congruence of two triangles
(D) RHS congruence of two right-angled triangles
Answer : (d)Show Answer :
Question 46: For two given triangles ABC and PQR, how many matchings are possible?
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) 6
(D) 3
Answer : (c)Show Answer :
Explanation : ABC ↔ PQR, ABC ↔ PRQ,
ABC ↔ QRP, ABC ↔ QPR,
ABC ↔ RPQ, ABC ↔ RQP.
Question 47: The symbol for congruence is
(A) ≡
(B) ≅
(C) ↔
(D) =
Answer : (b)Show Answer :
Question 48: The symbol for correspondence is
(A) =
(B) ↔
(C) ≡
(D) ≅
Answer : (b)Show Answer :
Question 49: If ∆ ABC = ∆ PQR, then
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D) none of these
Answer : (c)Show Answer :
Question 50: If ∆ ABC = ∆ PQR, then ∠A corresponds to
(A) ∠P
(B) ∠Q
(C) ∠R
(D) none of these
Answer : (a)Show Answer :
Question 51: We want to show that ∆ ART = ∆ PEN. We have to use SAS criterion. We have ∠ T = ∠ N, RT = EN. What more we need to show?
(A) PN = AT
(B) PN = AR
(C) PN = RT
(D) None of these
Answer : (a)Show Answer :
Question 52: We want to show that ∆ ART = ∆ PEN. We have to use ASA criterion. We have AT = PN, ∠ A = ∠ P. What more we need to show?
(A) ∠T = ∠N
(B) ∠T = ∠E
(C) ∠T = ∠P
(D) None of these
Answer : (a)Show Answer :
Question 53: Which congruence criterion do you use in the following?
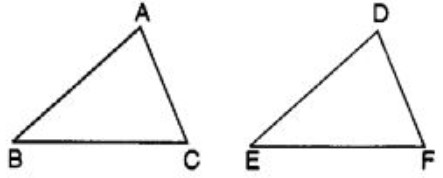
Given AC = DF
AB = DE
BC = EF
So, ∆ ABC ≅ ∆ DEF
(A) SSS
(B) SAS
(C) ASA
(D) RHS
Answer : (a)Show Answer :
Question 54: Which congruence criterion do you use in the following?
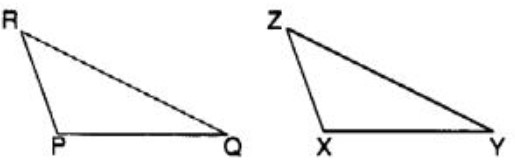
Given : ZX = RP
RQ = ZY
∠ PRQ = ∠ XZY
So, ∆ PRQ = ∆ XYZ
(A) SSS
(B) SAS
(C) ASA
(D) RHS
Answer : (b)Show Answer :
Question 55: Which congruence criterion do you use in the following?
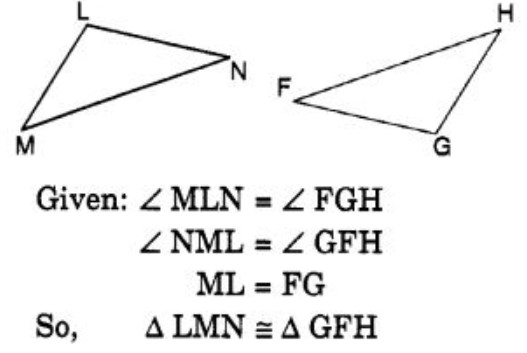
(A) SSS
(B) SAS
(C) ASA
(D) RHS
Answer : (c)Show Answer :
Question 56: Which congruence criterion do you use in the following?
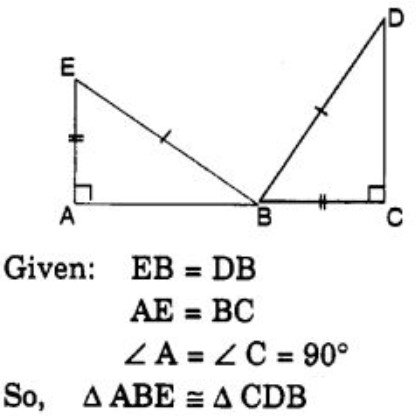
(A) SSS
(B) SAS
(C) ASA
(D) RHS
Answer : (d)Show Answer :
Question 57: In the following figure, the two triangles are congruent. The corresponding parts are marked. We can write ∆ RAT = ?
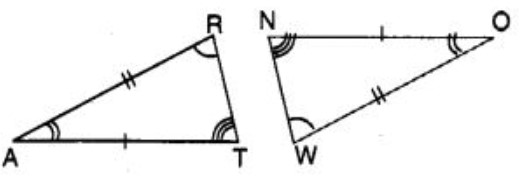
(A) ∆ WON
(B) ∆ WNO
(C) ∆ OWN
(D) ∆ ONW
Answer : (a)Show Answer :
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1: If two line segments have the same ……….. they are congruent.
Answer : lengthShow Answer :
Question 2: Among two congruent angles, one has a measure of 70°; the measures of the other angle is …………….
Answer : 70°Show Answer :
Question 3: When we write ∠A = ∠B, we actually mean ……………
Answer : m∠A = m∠BShow Answer :
Question 4: If two angles have the same …………. they are congruent.
Answer : measureShow Answer :
Question 5: Two triangles are congruent if they are …………… of each other and when ……………
(copies, superposed)
Answer : copies, superposedShow Answer :