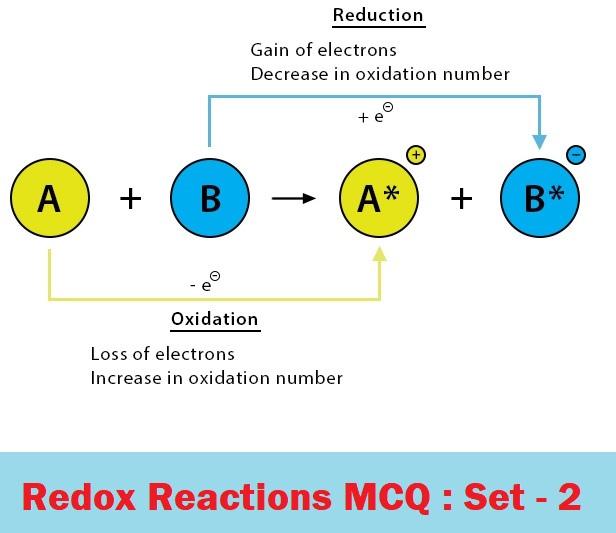
CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Redox Reactions Multiple Choice Questions with Answers. MCQ Questions Class 11 Chemistry Redox Reactions with Answers was Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 11 Chemistry Redox Reactions MCQs with Answers to know their preparation level.
Students who are searching for NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry Redox Reactions with Answers are compiled here to get good practice on all fundamentals. Know your preparation level on MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry with Answers. You can also verify your answers from our provided MCQ Class 11 Chemistry Redox Reactions with Answers. So, ace up your preparation with MCQ of Chapter 8 Chemistry Objective Questions.
MCQ Questions Class 11 Chemistry Redox Reactions with Answers - Set - 2
Question 1:
A standard reduction electrode potentials of four metals are A = -0.250 V, B = -0.140 V, C = -0.126 V, D = -0.402 V The metal that displaces A from its aqueous solution is:
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Correct Answer – (D)
Reduction potential of D is minimum i.e. −0.402 V. Thus oxidation potential of D is maximum i.e. to +0.402 V. D can oxidise itself and reduce other.
The aqueous solution A will be present in its ionic form and can be reduced by D as its reduction potential is higher than D.
Thus D can replace A from its Aqueous solution
Question 2 :
The oxidation number of Xe in BaXeO6 is
(a) 8
(b) 6
(c) 4
(d) 10
Correct Answer – (D)
Oxidation state of Ba in general = +2 and of O = −2
Applying formula, Sum of total oxidation state of all atoms = Overall charge on the compound.
Let oxidation state of Xe in BaXeO6 be x.
2 + x + 6(−2) = 0,
x = 10
But oxidation state 10 is not possible for Xe. In this case the oxidation state of Xe is equal to maximum possible oxidation state for Xe = +8
Question 3 :
The oxidation process involves
(a) Increase in oxidation number
(b) Decrease in oxidation number
(c) No change in oxidation number
(d) none of the above
Correct Answer – (A)
Oxidation process Involves:-
Addition of O2 or electronegative element
Removal of H/electropositive element
Loss of electrons
Increase in oxidation number
Question 4 :
What is n-factor?
(a) Equal to product of Number of moles of electrons when Lost or gained by one mole of reductant or oxidant
(b) When Number of moles of electrons Lost or gained by one mole of reductant or oxidant is not same.
(c) Equal to Number of moles of electrons Lost or gained by one mole of reductant or oxidant
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer – (C)
For redox reaction it is considered as change in their oxidation number or change in their reduction number in both side of a chemical reaction
Question 5 :
KMnO4 reacts with oxalic acid according to the equation 2MnO4– + 5C2O42- + 16H+ → 2Mn2+ +10CO2 + 8H2O Here 20 mL of 0.1 M KMnO4 is equivalent to
(a) 50 mL of 0.5 M C2H2O4
(b) 20 mL of 0.1 M C2H2O4
(c) 20 mL of 0.5 M C2H2O4
(d) 50 mL of 0.1 M C2H2O4
Correct Answer – (D)
2MnO4– + 5C2O42- + 16H+ → 2Mn2+ + 10CO2 + 8H2O
Therefore, 2 moles of MNO4– equivalent to 5 moles of C2O42-
20 mL of 0.1 M KMnO4 = 2 moles of KMnO4
Also, 50 mL of 0.1 M C2H2O4 equivalent to 5 mol of C2O42-
Therefore, these are equivalent
MCQ Questions Class 11 Chemistry Redox Reactions with Answers
Question 6 :
The colourless solution of silver nitrate slowly turns blue on adding copper chips to it because of
(a) Dissolution of Copper
(b) Oxidation of Ag+ → Ag
(c) Reduction of Cu2+ ions
(d) Oxidation of Cu atoms
Correct Answer – (D)
When copper turnings are added to silver nitrate solution, the solution becomes brown in color after sometime because copper is more reactive than silver so it displaces silver from silver nitrate solution and form copper nitrate solution
Question 7 :
Metals generally react with dilute acids to produce hydrogen gas. Which one of the following metals does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid?
(a) Copper
(b) Magnesium
(c) Iron
(d) Silver
Correct Answer – (B)
Most of the metals such as Al, Cu, Fe etc. reacts with dilute acids to produce hydrogen gas but magnesium is an exception. Magnesium being an active metal liberates dihydrogen gas as it is allowed to react with dilute HCl. Thus all the given metals react with dilute acids.
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Question 8 :
The oxidation number of Mn is maximum in
(a) MnO2
(b) K2MnO4
(c) Mn3O4
(d) KMnO4.
Correct Answer – (D)
The electronic configuration of Mn is:
Mn(25) = [Ar]3d5 4s2, 4p0
In excited state, it can lose its all 7 electrons.
Hence, maximum oxidation sate exhibited by Mn is +7 which is in KMnO4
Question 9 :
One mole of N2H4 loses ten moles of electrons to form a new compound A. Assuming that all the nitrogen appears in the new compound, what is the oxidation state of nitrogen in A? (There is no change in the oxidation state of hydrogen.)
(a) -1
(b) -3
(c) +3
(d) +5
Correct Answer – (C)
First to find oxidation number of Nitrogen in N2H4
Oxidation number of H = +1
Let oxidation number of nitrogen be x
2x + 4(1) = 0
2x = -4
x = -2
Each nitrogen atom has -2 oxidation number. So taken both nitrogen atoms in account gives oxidation number -4.
Change in oxidation number of nitrogen on losing 10 mol of electrons (considering no change in oxidation number of hydrogen atoms)
-4 – (-10) = +6
Therefore, oxidation number of 2 nitrogen atoms in compound Y is +6. Hence, oxidation number of each nitrogen atom will be +3 in new compound Y
Question 10 :
Which of the following reactions does not involve either oxidation or reduction?
(a) VO2+ → V2O3
(b) Na → Na+
(c) CrO2-4 → Cr2O2-7
(d) Zn2+ →Zn
Correct Answer – (C)
In VO2+ →V2O3, V is reduced from +4 to +3 oxidation state.
In Na → Na2+, Na is oxidised from to +1 oxidation state.
In CrO4-2 → Cr2O7-2, Cr remains in same oxidation state +6.
In Zn+2 → Zn, Zn is reduced from +2 to 0 oxidation state
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 : Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 : Structure Of The Atom
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 3 : Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 : Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 : States of Matter
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 : Thermodynamics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 : Equilibrium
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 : Redox Reactions
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 : Hydrogen
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 : The s-Block Elements
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 : The p-Block Elements
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 : Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 : Hydrocarbons
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 : Environmental Chemistry