Class 9 Mathematics MCQ Probability with Answers is Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 9 Mathematics MCQ Probability with Answers to know their preparation level.
Students who are searching for NCERT Class 9 Mathematics MCQ Probability with Answers are compiled here to get good practice on all fundamentals. Know your preparation level on MCQ Questions for Class 9 Mathematics MCQ Probability with Answers. You can also verify your answers from the provided Class 9 Mathematics MCQ Probability with Answers. So, ace up your preparation with MCQ of Class 9 Mathematics MCQ & NCERT Textbook solutions Examinations.
NCERT Class 9 Mathematics MCQ Probability with Answers
Question :The probability of an event of a trial is always
(a) more than 1
(b) between 0 and 1 (both inclusive)
(c) 1
(d) 0
Answer : (b) between 0 and 1 (both inclusive)Show Answer :
Question :A standard deck of 52 cards is shuffled. One card is drawn at random. The probability that the card is red or an ace is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (a) Show Answer :
Question : The probability of each event, when a coin is tossed for 1000 times with frequencies: Head:455 & Tail: 545 is:
(a) 0.455 & 0.545
(b) 0.5 & 0.5
(c) 0.45 & 0.55
(d) 455 & 545
Answer : aShow Answer :
Explanation: Let E and F are the event of the occurrence of Head and Tail, respectively.
Probability of Occurrence of Head P(E) = No. of heads/total number of trials
P(E) = 455/1000 = 0.455
Similarly,
P(F) = No. of tails/total number of trials
P(F) = 545/1000 = 0.545
Question : The sum of all probabilities equal to:
(a) 4
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 2
Answer : bShow Answer :
Question : The probability of each event lies between:
(a) 1 & 2
(b) 1 & 10
(c) 0 & 1
(d) 0 & 5
Answer : cShow Answer :
Question : If P(E) = 0.44, then P(not E) will be:
(a) 0.44
(b) 0.55
(c) 0.50
(d) 0.56
Answer : dShow Answer :
Explanation: We know;
P(E) + P(not E) = 1
0.44 + P(not E) = 1
P(not E) = 1 – 0.44 = 0.56
Question : If P(E) = 0.38, then probability of event E, not occurring is:
(a) 0.62
(b) 0.38
(c) 0.48
(d) 1
Answer : aShow Answer :
Explanation: P(not E) = 1 – P(E) = 1-0.38 = 0.62
Question : The probability of drawing an ace card from a deck of cards is:
(a) 1/52
(b) 1/26
(c) 4/13
(d) 1/13
Answer : dShow Answer :
Explanation: There are 4 aces in a deck of card.
Hence, the probability of taking one ace out of 52 cards = 4/52 = 1/13
Question : If the probability of an event to happen is 0.3 and the probability of the event not happening is:
(a) 0.7
(b) 0.6
(c) 0.5
(d) None of the above
Answer : aShow Answer :
Explanation: Probability of an event not happening = 1 – P(E)
P(not E) = 1 – 0.3 = 0.7
Question : A dice is thrown. The probability of getting 1 and 5 is:
(a) ⅙
(b) ⅔
(c) ⅓
(d) ½
Answer : cShow Answer :
Explanation: The probability of getting 1 and 5 = 2/6 = ⅓
Question :Gugu throws a die once. The probability that she shows a number less than 5 is :
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (a) Show Answer :
Question :The maximum probability of an event of a trial is:
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) Lies between 0 and 1.
(d) -1
Answer : (b) 1Show Answer :
Question :A and B throw a pair of dice. If A throws 9, then B’s chance of throwing a higher number is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (a) Show Answer :
Question :The probability of an impossible event is
(a) more than 1
(b) less than 1
(c) 1
(d) 0
Answer : (d) 0Show Answer :
Question :Three unbiased coins are tossed together. The probability of getting at least two heads is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) 1
Answer : (b) Show Answer :
Question :The probability of getting 53 Sundays in a leap year is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (a) Show Answer :
Question :In a simultaneous throw of a pair of dice, the probability of getting a sum more than 7 will be
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (a) Show Answer :
Question :Three unbiased coins are tossed. What is the probability of getting at most two heads?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (a) Show Answer :
Question :Which one of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
(a)
(b)
(c) 0
(d) 1
Answer : (b) Show Answer :
Question :Two unbiased coins are tossed. What is probability of getting at most one tail?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (d) Show Answer :
Question :Two unbiased coins are tossed simultaneously. The probability of getting at most one head is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (c) Show Answer :
Question :A die is thrown 300 times and odd numbers are obtained 153 times. Then, the probability of getting an even number is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (b) Show Answer :
Question :The sum of the probabilities of All events of a trial is
(a) 1
(b) between 0 and 1
(c) less than 1
(d) greater than 1
Answer : (b) between 0 and 1Show Answer :
Question : Performing an event once is called
(a) Sample
(b) Trial
(c) Error
(d) None of the above
Answer :bShow Answer :
Explanation: Performing an event once is called a trial.
Question : A card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. What is the probability of getting a king of the red suits?
(a) 3/36
(b) 1/26
(c) 3/26
(d) 1/16
Answer :bShow Answer :
Explanation: In a pack of 52 cards, there are a total of 4 king cards, out of which 2 are red and 2 are black.
Therefore, in a red suit, there are 2 king cards.
Hence, the probability of getting a king of red suits = 2/52 = 1/26.
Question : Find the probability of a selected number is a multiple of 4 from the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …15.
(a) 1/5
(b) 1/3
(c) 4/12
(d) 2/15
Answer :aShow Answer :
Explanation: S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15}
Multiples of 4 from the sample space = {4, 8, 12}
Therefore, the probability of the selected number is a multiple of 5 is 3/15 = 1/5.
Question : What is the probability of drawing a queen from the deck of 52 cards?
(a) 1/26
(b) 1/52
(c) 1/13
(d) 3/52
Answer :cShow Answer :
Explanation: Total cards = 52
Number of queens in a pack of 52 cards = 4
Hence, the probability of drawing a queen from a deck of 52 cards = 4/52 = 1/13
Question : Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) 0.75
(d) 1.3
Answer :dShow Answer :
Explanation: The probability of an event always lies between 0 and 1.
Question : There are 4 green and 2 red balls in a basket. What is the probability of getting the red balls?
(a) 1/2
(b) 1/3
(c) 1/5
(d) 1/6
Answer :bShow Answer :
Explanation: Total balls = 4 green + 2 red = 6 balls
No. of red balls = 2.
Hence, the probability of getting the red balls = 2/6 = 1/3
Question : Empirical probability is also known as
(a) Classic probability
(b) Subjective probability
(c) Experimental probability
(d) None of the above
Answer :cShow Answer :
Explanation: Empirical probability is also known as experimental probability.
Question : If two coins are tossed simultaneously, then what is the probability of getting exactly two tails?
(a) 1/4
(b) 1/2
(c) 1/3
(d) None of the above
Answer :aShow Answer :
Explanation: If two coins are tossed, then the sample space, S = {HH, HT, TH, TT}
Question : Packets of salt, each marked 2 kg, actually contained the following weights (in kg) of salt :1.980, 2.000, 2.025, 1.850, 1.990, 2.040, 1.950, 2.050, 2.060, 1.980, 2.030, 1.970Out of these packets one packet is chosen at random.The probability that the chosen packet contains less than 2 kg of salt is
(a) 1/12
(b) 1/4
(c) 1/3
(d) 1/2
Answer 😀Show Answer :
Question : Three coins are tossed simultaneously 200 times with following outcomes :

The probability of getting two heads is
(a) 23/25
(b) 9/25
(c) 18/25
(d) 4/5
Answer :BShow Answer :
Question : A die is thrown 225 times and the results were as follows :
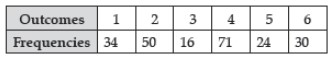
The probability of getting a prime number is
(a) 8/45
(b) 2/5
(c) 24/225
(d) 124/225
Answer :BShow Answer :
Question : The salaries of 150 employees in an office are given below :
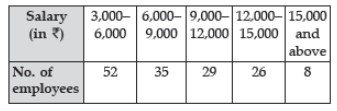
An employee is selected at random. The probability that his salary is Rs 6,000 or more but less than Rs 12,000 is
(a) 7/30
(b) 32/75
(c) 29/150
(d) 58/75
Answer :BShow Answer :
Question : In an experiment a coin is tossed 500 times. If the head turns up 280 times, the experimental probability of getting a head is
(a) 14/25
(b) 11/25
(c) 13/25
(d) 19/25
Answer :AShow Answer :
Question : In a section of class IX having 40 students, the following blood groups are recorded :
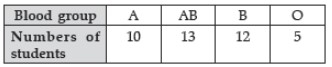
A student is selected at random from the class. The probability that he/she has blood group B, is
(a) 1/4
(b) 13/40
(c) 3/10
(d) 1/8
Answer :CShow Answer :
Question : A machine generated these 10 codes :{0A1, AAA, ABC, 2B1, 3B7, BB2, 1AC, 111, 222, 333}.A code is drawn at random to allot an employee. The probability that the code have at least two digits is
(a) 2/5
(b) 3/5
(c) 4/5
(d) None of these
Answer :BShow Answer :
Question : A die is thrown 200 times simultaneously, and the frequencies of various outcomes are given below :

The probability of getting 5 is
(a) 1/40
(b) 13/40
(c) 11/40
(d) 1/5
Answer :BShow Answer :
Question : In a cricket match, a batsman hits a boundary 4 times out of 25 balls, he plays. The probability that he hits a boundary is
(a) 4/25
(b) 21/25
(c) 25/4
(d) 25/21
Answer :AShow Answer :
Question : In a sample study of 642 people, it was found that 514 people have a high school certificate. If a person is selected at random, the probability that the person has a high school certificate is
(a) 0.5
(b) 0.6
(c) 0.7
(d) 0.8
Answer 😀Show Answer :
Question : The following table shows the blood groups of 60 students of a class :
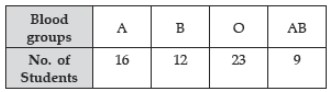
One student of the class is chosen at random. What is the probability that the chosen student has either blood group A or B?
(a) 1/5
(b) 1/30
(c) 7/15
(d) 17/30
Answer :CShow Answer :
Question : A coin is tossed 100 times and head appears 64 times. The probability of getting a tail is
(a) 18/25
(b) 9/25
(c) 0
(d) 1
Answer :BShow Answer :
Question :One card is drawn at random from a pack of 52 cards. What is the probability that the card drawn is either a red card or a king?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (c) Show Answer :
Question :In a series of 6 cricket matches, the number of runs scored by the captain of a team are 54, 32, 48, 55, 29, 35. So in the next match, the probability that he will cross the half century is
(a) 0.33
(b) 0.24
(c) 0.35
(d) 0.48
Answer : (a) 0.33Show Answer :
Question : The probability of an event of a trial is always
(a) more than 1
(b) between 0 and 1 (both inclusive)
(c) 1
(d) 0
Answer :(b) between 0 and 1Show Answer :
Question : The sum of all probabilities equal to:
(a) 4
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 2
Answer :(b) 1Show Answer :
Question : A and B throw a pair of dice. If A throws 9, then B’s chance of throwing a higher number is
(a) 1/6
(b) 1/9
(c) 1/3
(d) 2/9
Answer :(a) 1/6Show Answer :
Question : A standard deck of 52 cards is shuffled. One card is drawn at random. The probability that the card is red or an ace is
(a) 7/13
(b) 5/15
(c) 13/7
(d) 2/13
Answer :(a) 7/13Show Answer :
Question : The probability of an impossible event is
(a) more than 1
(b) less than 1
(c) 1
(d) 0
Answer :(d) 0Show Answer :
Question : If P(E) = 0.44, then P(not E) will be:
(a) 0.44
(d) 0.55
(c) 0.50
(d) 0.56
Answer :(d) 0.56Show Answer :
Question : A die is thrown 300 times and odd numbers are obtained 153 times. Then, the probability of getting an even number is
(a) 174/300
(b) 147/300
(c) 147/153
(d) 153/300
Answer :(b) 147/300Show Answer :
Question : Two dice are tossed. The probability of getting two 5’s is
(a) 1/18
(b) 1/6
(c) 1/36
(d) 1/2
Answer :(c) 1/36Show Answer :
Question : A dice is thrown. The probability of getting 1 and 5 is:
(a) ⅙
(b) ⅔
(c) ⅓
(d) ½
Answer :(c) ⅓Show Answer :
Question :A card is selected at random from a deck of 52 cards. The probability of its being a red face card is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (d) Show Answer :
Question :An unbiased dice is thrown. What is the probability of getting an even number or a multiple of 3?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (a) Show Answer :
Question :What is the probability that a leap year has 53 Sundays?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (d) Show Answer :
Question :Probability of boy that he will get married with his girlfriend is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (a) Show Answer :
Question :In a football match, a player hits 8 goals out of 60 balls. Find the probability that the player did not hit the goal.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer : (d) Show Answer :
Question : In a football match, a player hits 8 goals out of 60 balls. Find the probability that the player did not hit the goal.
(a) 11/15
(b) 4/5
(c) 8/15
(d) 13/15
Answer :(d) 13/15Show Answer :
Question : Three unbiased coins are tossed together. The probability of getting at least two heads is
(a) 3/8
(b) 1/2
(c) 1/8
(d) 1
Answer :(b) 1/2Show Answer :
Question : A batsman hits boundaries for 6 times out of 30 balls. Find the probability that he did not hit the boundaries.
(a) ⅕
(b) ⅖
(c) ⅗
(d) ⅘
Answer :(d) ⅘Show Answer :
Question : Three unbiased coins are tossed. What is the probability of getting at most two heads?
(a) 7/8
(b) 3/4
(c) 5/6
(d) 3/2
Answer :(a) 7/8Show Answer :
Question : A bag contains 5 red balls and some blue balls. The probability of drawing a blue ball is double that of a red ball. The number of blue balls in the bag is
(a) 5
(b) 10
(c) 20
(d) 30
Answer :(b) 10Show Answer :
Question : A batsman hits boundaries for 6 times out of 30 balls. Find the probability that he did not hit the boundaries.
(a) ⅕
(b) ⅖
(c) ⅗
(d) ⅘
Answer : dShow Answer :
Explanation: No. of boundaries = 6
No. of balls = 30
No. of balls without boundaries = 30 – 6 =24
Probability of no boundary = 24/30 = ⅘
Question : Three coins were tossed 200 times. The number of times 2 heads came up is 72. Then the probability of 2 heads coming up is:
(a) 1/25
(b) 2/25
(c) 7/25
(d) 9/25
Answer : dShow Answer :
Explanation: Probability = 72/200 = 9/25
Question : What is the probability of getting an odd number less than 4, if a die is thrown?
(a) 1/6
(b) 1/2
(c) 1/3
(d) 0
Answer :cShow Answer :
Explanation: Sample space, S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Favourable outcomes = {1, 3}
Therefore, the probability of getting an odd number less than 4 = 2/6 = ⅓.
Question : What is the probability of impossible events?
(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) More than 1
(d) Less than 1
Answer :bShow Answer :
Explanation: The probability of an impossible event is always 0.






One Reply to “Class 9 Mathematics MCQ Probability”