Class 9 Mathematics MCQ Coordinate Geometry with Answers is Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 9 Mathematics MCQ Coordinate Geometry with Answers to know their preparation level.
Students who are searching for NCERT Class 9 Mathematics MCQ Coordinate Geometry with Answers are compiled here to get good practice on all fundamentals. Know your preparation level on MCQ Questions for Class 9 Mathematics MCQ Coordinate Geometry with Answers. You can also verify your answers from the provided Class 9 Mathematics MCQ Coordinate Geometry with Answers. So, ace up your preparation with MCQ of Class 9 Mathematics MCQ & NCERT Textbook solutions Examinations.
NCERT Class 9 Mathematics MCQ Coordinate Geometry with Answers
Question :The point (–2, –3) belongs to Quadrant :
(a) Q1
(b) Q2
(c) Q3
(d) Q4
Answer : (c) Q3Show Answer :
Question :The abscissa or x-coordinate of any point on Y-axis is:
(a) Three
(b) Two
(c) One
(d) Zero
Answer : (d) ZeroShow Answer :
Question :The point which lies on y-axis at a distance of 6 units in the positive direction of y-axis is
(a) (-6, 0)
(b) (0, -6)
(c) (0, 6)
(d) (6, 0)
Answer : (c) (0, 6)Show Answer :
Question :The point A(3, 4) lies in
(a) II Quadrant
(b) I Quadrant
(c) IV Quadrant
(d) III Quadrant
Answer : (b) I QuadrantShow Answer :
Question :The name of horizontal line in the cartesian plane which determines the position of a point is called:
(a) Origin
(b) X-axis
(c) Y-axis
(d) Quadrants
Answer : (b) X-axisShow Answer :
Question : The point (–2, 0) lies on :
(a) +ve x-axis
(b) +ve y-axis
(c) –ve x-axis
(d) –ve y-axis
Answer :(c) –ve x-axisShow Answer :
Question : If the coordinates of a point are (3, 0), then it lies in:
(a) X-axis
(b) Y-axis
(c) At origin
(d) Between x-axis and y-axis
Answer :(a) X-axisShow Answer :
Question : The points (-5, 2) and (2, -5) lie in the
(а) same quadrant
(b) II and III quadrant respectively.
(c) II and IV quadrant respectively.
(d) I and IV quadrant respectively.
Answer :(c) II and IV quadrant respectively.Show Answer :
Question : The name of horizontal line in the cartesian plane which determines the position of a point is called:
(a) Origin
(b) X-axis
(c) Y-axis
(d) Quadrants
Answer :(b) X-axisShow Answer :
Question :Ordinate of all the points in the x-axis is:
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) –1
(d) Any natural number
Answer : (a) 0Show Answer :
Question :The name of vertical line in the cartesian plane which determines the position of a point is called:
(a) Origin
(b) X-axis
(c) Y-axis
(d) Quadrants
Answer : (c) Y-axisShow Answer :
Question :The point (3, 0) lies on :
(a) +ve x-axis
(b) +ve y-axis
(c) –ve x-axis
(d) –ve y-axis
Answer : (a) +ve x-axisShow Answer :
Question :Find the coordinates of the point equidistant from the points A(1, 2), B (3, –4) and C(5, –6).
(a) (12, 3)
(b) (11, 2)
(c) (10, 2)
(d) (11, 3)
Answer : (b) (11, 2)Show Answer :
Question :The section formed by horizontal and vertical lines determining the position of point in a cartesian plane is called:
(a) Origin
(b) X-axis
(c) Y-axis
(d) Quadrants
Answer : (d) QuadrantsShow Answer :
Question :If the abscissa of a point is y and the ordinate is x then the coordinates of the point are _______
(a) (x, 0)
(b) (y, x)
(c) (x, y)
(d) (0, y)
Answer : (b) (y, x)Show Answer :
Question :The point of intersection of X and Y axes is called :
(a) Origin
(b) Null point
(c) Common point
(d) None of these
Answer : (a) OriginShow Answer :
Question :If the coordinates of a point are (3, 0), then it lies in:
(a) X-axis
(b) Y-axis
(c) At origin
(d) Between x-axis and y-axis
Answer : (a) X-axisShow Answer :
Question :The coordinates of any point on the y-axis are of the form (0, k), where |k| is the distance of the point from the:
(a) y-axis
(b) x-axis
(c) (0, 1)
(d) (1, 0)
Answer : (b) x-axisShow Answer :
Question :Find the ratio in which the line joining the points (6, 4) and (1, –7) is divided by x-axis.
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 2 : 7
(c) 4 : 7
(d) 6 : 7
Answer : (c) 4 : 7Show Answer :
Question :Abscissa of all points on the x-axis is
(a) -1
(b) 0
(c) any number
(d) 1
Answer : (c) any numberShow Answer :
Question :Abscissa of a point is positive in:
(a) I and II quadrants
(b) I and IV quadrants
(c) I quadrant only
(d) II quadrant only
Answer : (b) I and IV quadrantsShow Answer :
Question :The points (a, a) (–a, a) and (– (√3) a, (√3)a) form the vertices of an :
(a) Scalene triangle
(b) Right angled triangle
(c) Isosceles Right angled triangle
(d) Equilateral triangle
Answer : (d) Equilateral triangleShow Answer :
Question :The point (–2, 0) lies on :
(a) +ve x-axis
(b) +ve y-axis
(c) –ve x-axis
(d) –ve y-axis
Answer : (c) –ve x-axisShow Answer :
Question :If the x-coordinate of a point is zero, then this point lies:
(a) In II quadrant
(b) In I quadrant
(c) On x-axis
(d) On y-axis
Answer : (d) On y-axisShow Answer :
Question :On plotting P (–3, 8), Q (7, –5), R (–3, –8) and T (–7, 9) are plotted on the graph paper, then point(s) in the third quadrant are:
(a) P and T
(b) Q and R
(c) Only R
(d) P and
Answer : (c) Only RShow Answer :
Question :The point (0, 9) lies
(a) in quadrant IV
(b) on the positive direction of y-axis
(c) in quadrant III
(d) on the positive direction of x-axis
Answer : (b) on the positive direction of y-axisShow Answer :
Question :. If Mohit wants to stand in such a way that he is equidistance from each of the four students A, B, C and D then what are the coordinate of his position ?
(a) (6, 6)
(b) (7, 5)
(c) (6, 4)
(d) (4, 6)
Answer :BShow Answer :
Question : The coordinates of the mid-points of the sides of a triangle are (4, 2), (3, 3) and (2, 2). What will be the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle?

Answer :AShow Answer :
Question :Area of quadrilateral formed by the vertices (–1, 6), (–3, –9), (5, –8) and (3, 9) is _______ (sq. units).
(a) 96
(b) 18
(c) 50
(d) 25
Answer :AShow Answer :
Question : Find the area of triangle whose vertices are (t, t – 2), (t + 2, t + 2) and (t + 3, t).
(a) 14 sq. units
(b) 2t sq. units
(c) 5 sq. units
(d) 4 sq. units
Answer 😀Show Answer :
Question : The vertices of a DABC are A(2,1), B(6, –2), C(8, 9). If AD is angle bisector, where D meets on BC, then coordinates of D are _______.
(A) (20/3, 5.3)
(b) (5, 2)
(c) (4, 3)
(d) (14, 3, 7/3)
Answer :AShow Answer :
Question : The coordinates of the third vertex of an equilateral triangle whose two vertices are at (3, 4), (–2, 3) are ________.
(A) (1, 7)
(b) (5, 1)
(c) (1+√3/2, 7-5√3/2) or (1-√3/2, 7 + 5√3/2)
(d) (-5, 5)
Answer :CShow Answer :
Question : A well planned locality, has two straight roads perpendicular to each other. There are 5 lanes parallel to Road – I. Each lane has 8 houses as seen in figure. Chaitanya lives in the 6th house of the 5th lane and Hamida lives in the 2nd house of the 2nd lane. What will be the shortest distance between their houses?
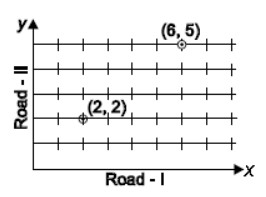
(A) 10 units
(b) 12 units
(c) 6 units
(d) 5 units
Answer :AShow Answer :
Question : To raise social awareness about the hazards of smoking, a school decided to start “No smoking campaign”. A student is asked to prepare a campaign banner in the shape of a triangle shown in the figure. If cost of 1 cm2 of banner is ₹ 2, find the cost of the banner.
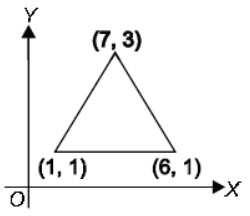
(A) 12 (B)6
(c) 5 (D)10
Answer 😀Show Answer :
Question : The coordinates of the centre of a circlepassing through (1, 2), (3, – 4) and (5, – 6)is ________.
(a) (2, 11)
(b) (11, 2)
(c) (11, – 2)
(d) (– 2, 11)
Answer :AShow Answer :
Question : If A(2, 2), B(4, 4) and C(2, 6) are the verticesof a triangle ABC and D, E and F are themid point of AB, BC and AC respectively,then
(i) Find the area of ΔABC.
(b) Find the area of ΔDEF.
(c) Find the ratio of area of ΔDEF to ΔABC.
(i) (ii) (iii)
(a) 8 sq. units 2 sq. units 1 : 4
(b) 6 sq. units 3 sq. units 1 : 2
(c) 4 sq. units 1 sq. units 1 : 4
(d) 3 sq. units 1 sq. units 1 : 3
Answer :CShow Answer :
Question :The values of t, if the area of the pentagonABCDE be 45 / 2sq. units where A = (1, 3),B = (–2, 5), C = (–3, –1), D = (0, –2) andE = (2, t) are ________.
(a) –1, 17
(b) –1, 106
(c) 1, 17
(d) 1, 18
Answer :AShow Answer :
Question :If (–2, 1), (a, 0), (4, b) and (1, 2) arethe vertices of a parallelogram, then
(i) Find a
(b) Find b
(c) Area of the parallelogram.
(i) (ii) (iii)
(a) 1 –1 10 sq. units
(b) 1 –2 6 sq. units
(c) 1 1 6 sq. units
(d) –1 –1 6 sq. units
Answer :CShow Answer :
Question : Points (1, -1), (2, -2), (4, -5), (-3, -4)
(a) lie in II quadrant
(b) lie in III quadrant
(c) lie in IV quadrant
(d) Does not lie in the same quadrant
Answer :dShow Answer :
Explanation: The point (1, -1), (2, -2) and (4, -5) lies in the fourth quadrant, where (-3, -4) lies in the third quadrant.
Question : Abscissa of all the points on the y-axis is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) -1
(d) Any number
Answer :aShow Answer :
Explanation: The abscissa of all the points on the y-axis is 0. We know that the coordinates of any point on the y-axis is (0, y). Here, the ordinate can take any value and the abscissa is zero.
Question : Ordinate of all the points on the y-axis is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) -1
(d) Any number
Answer :dShow Answer :
Explanation: The ordinate of all the points on the y-axis can be any number. The coordinates of any point on the y-axis is (0, y). Here, abscissa can take only the value of 0 and the ordinate can take any value.
Question : The point which lies on the y-axis at a distance of 5 units in the negative direction of the y-axis is
(a) (5, 0)
(b) (0, 5)
(c) (-5, 0)
(d) (0, -5)
Answer :dShow Answer :
Explanation: The coordinates of any point on the y-axis is (0, y).
Hence, abscissa should be 0.
Given that, the point lies in the negative direction of the y-axis. Hence, the value of y should be negative.
Therefore, the point which lies on the y-axis at a distance of 5 units in the negative direction is (0, -5).
Question : If the coordinates of a point are (3, 0), then it lies in:
(a) X-axis
(b) Y-axis
(c) At origin
(d) Between x-axis and y-axis
Answer : aShow Answer :
Explanation: Since, x = 3 and y = 0, therefore, the point will lie at the positive x-axis 3 units far from the origin.
Question : If the coordinates of a point are (-3, 4), then it lies in:
(a) First quadrant
(b) Second quadrant
(c) Third quadrant
(d) Fourth quadrant
Answer : bShow Answer :
Explanation: Since x = -3 and y = 4, then if we plot the point in a plane, it lies in the second quadrant.
Question : If the coordinates of a point are (-3, -4), then it lies in:
(a) First quadrant
(b) Second quadrant
(c) Third quadrant
(d) Fourth quadrant
Answer : cShow Answer :
Explanation: Since, x = -3 and y = -4, then if we plot the point in a plane, it lies in the third quadrant.
Question : Points (1, 2), (-2, -3), (2, -3);
(a) First quadrant
(b) Do not lie in the same quadrant
(c) Third quadrant
(d) Fourth quadrant
Answer : bShow Answer :
Question : If x coordinate of a point is zero, then the point lies on:
(a) First quadrant
(b) Second quadrant
(c) X-axis
(d) Y-axis
Answer : dShow Answer :
Question : Signs of the abscissa and ordinate of a point in the second quadrant are respectively
(a) +, +
(b) +, –
(c) -, +
(d) -, –
Answer :cShow Answer :
Explanation: The signs of abscissa (x-value) and ordinate(y-value) in the second quadrant are – and + respectively.
Question : The point (-10, 0) lies in
(a) Third quadrant
(b) Fourth quadrant
(c) On the negative direction of the x-axis
(d) On the negative direction of the y-axis
Answer :cShow Answer :
Explanation: The point (-10, 0) lies in the negative direction of the x-axis.
Question : A quadrant in which both x and y values are negative is
(a) First quadrant
(b) Second quadrant
(c) Third quadrant
(d) Fourth quadrant
Answer :cShow Answer :
Explanation: In the third quadrant, both the abscissa and ordinate values are negative. Example (-2, -2), which lies in the third quadrant.
Question : Abscissa of all the points on the x-axis is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) Any number
Answer :dShow Answer :
Explanation: Abscissa of all the points on the x-axis can be any number. The coordinates of any point on the x-axis is (x, 0), where x can take any value.
Question : Ordinate of all points on the x-axis is
(a) -1
(b) 0
(c) 1
(d) Any number
Answer :bShow Answer :
Explanation: The ordinate of all points on the x-axis is 0. We know that the coordinates of any point on the x-axis is (x, 0). Here, the abscissa can take any value and the ordinate is zero.
Question : Abscissa of a point is positive in
(a) I quadrant
(b) I and II quadrants
(c) II quadrant only
(d) I and IV quadrants
Answer :dShow Answer :
Explanation: In a coordinate plane, x can take positive values in the first and fourth quadrants. For example, (2, 2) and (2, -4) lie on the first and fourth quadrants, respectively.
Question :If x coordinate of a point is zero, then the point lies on:
(a) First quadrant
(b) Second quadrant
(c) X-axis
(d) Y-axis
Answer : (d) Y-axisShow Answer :
Question : The co-ordinates of the origin are
(a) (2, 0)
(b) (0, 2)
(c) (0, 0)
(d) (2, 2)
Answer :(c) (0, 0)Show Answer :
Question : Ordinate of all the points in the x-axis is:
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) –1
(d) Any natural number
Answer :(a) 0Show Answer :
Question : If the coordinates of a point are (-3,-4), then it lies in:
(a) First quadrant
(b) Second quadrant
(c) Third quadrant
(d) Fourth quadrant
Answer :(c) Third quadrant Show Answer :
Question : Mirror image of the point (9, -8) in y-axis is
(a) (-9, -8)
(b) (9, 8)
(c) (-9, 8)
(d) (-8, 9)
Answer :(a) (-9, -8)Show Answer :
Question : The point which lies on y-axis at a distance of 6 units in the positive direction of y-axis is
(a) (-6, 0)
(b) (0, -6)
(c) (0, 6)
(d) (6, 0)
Answer :(c) (0, 6)Show Answer :
Question : The abscissa or x-coordinate of any point on Y-axis is:
(a) Three
(b) Two
(c) One
(d) Zero
Answer :(d) ZeroShow Answer :
Question : The section formed by horizontal and vertical lines determining the position of point in a cartesian plane is called:
(a) Origin
(b) X-axis
(c) Y-axis
(d) Quadrants
Answer :(d) QuadrantsShow Answer :
Question : The name of vertical line in the cartesian plane which determines the position of a point is called:
(a) Origin
(b) X-axis
(c) Y-axis
(d) Quadrants
Answer :(c) Y-axisShow Answer :
Question : If the points A(2, 0), B(-6, 0) and C(3, a – 3) lie on the x-axis, then the value of a is
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) -6
Answer :(c) 3Show Answer :
Question : Find the coordinates of the point equidistant from the points A(1, 2), B (3, –4) and C(5, –6).
(i) (12, 3)
(b) (11, 2)
(c) (10, 2)
(d) (11, 3)
Answer :(b) (11, 2)Show Answer :
Question : If (2, 2p + 2) is the mid-point of (3p, 4) and (-2, 2q), then the value of p and q are
(a) 3, 6
(b) 7, 9
(c) 2, 4
(d) 8, 10
Answer :(c) 2, 4Show Answer :
Question : The point of intersection of X and Y axes is called :
(a) Origin
(b) Null point
(c) Common point
(d) None of these
Answer :(a) OriginShow Answer :
Question : Points (1,2), (-2,-3), (2,-3);
(a) First quadrant
(b) Do not lie in the same quadrant
(c) Third quadrant
(d) Fourth quadrant
Answer :(b) Do not lie in the same quadrantShow Answer :
Question : Find the ratio in which the line joining the points (6, 4) and (1, –7) is divided by x-axis.
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 2 : 7
(c) 4 : 7
(d) 6 : 7
Answer :(c) 4 : 7Show Answer :
Question : A point of the form (0, (ii) lies on
(a) x- axis
(b) quadrant III
(c) quadrant I
(d) y- axis
Answer :(d) y- axisShow Answer :
Question : Abscissa of all points on the x-axis is
(a) -1
(b) 0
(c) any number
(d) 1
Answer :(c) any numberShow Answer :
Question : Ordinate of all the points in the x-axis is:
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) –1
(d) Any natural number
Answer :(a) 0Show Answer :
Question : The mirror image of the point (-3, -4) in x-axis is
(a) (-4, -3)
(b) (3, -4)
(c) (3, 4)
(d) (-3, 4)
Answer :(d) (-3, 4)Show Answer :
Question : The point M lies in the IV quadrant. The coordinates of point M are
(a) (a, (ii)
(b) (-a, (ii)
(c) (a, -(ii)
(d) (-a, -(ii)
Answer :(c) (a, -(ii)Show Answer :
Question : The point (0, 9) lies
(a) in quadrant IV
(b) on the positive direction of y-axis
(c) in quadrant III
(d) on the positive direction of x-axis
Answer :(b) on the positive direction of y-axisShow Answer :
Question : The points (a, (i) (–a, (i) and (– (√3) a, (√3)(i) form the vertices of an :
(a) Scalene triangle
(b) Right angled triangle
(c) Isosceles Right angled triangle
(d) Equilateral triangle
Answer :(d) Equilateral triangleShow Answer :
Question : The coordinates of any point on the y-axis are of the form (0, k), where |k| is the distance of the point from the:
(a) y-axis
(b) x-axis
(c) (0, 1)
(d) (1, 0)
Answer :(b) x-axisShow Answer :
Question : The points (–4,–8) lies in:
(a) First quadrant
(b) Second quadrant
(c) Third quadrant
(d) Fourth quadrant
Answer :(d) Fourth quadrantShow Answer :
Question : The number of parts the coordinates axes divide the plane is
(a) Two parts
(b) Four parts
(c) Six parts
(d) Eight parts
Answer :(b) Four partsShow Answer :
Question : Points (6, 8), (3, 7), (–2, –2) and (1, –1) are joined to form a quadrilateral. What will be the structure of quadrilateral?
(a) Rhombus
(b) Parallelogram
(c) Square
(d) Rectangle
Answer :BShow Answer :
Question : Find the area (in square units) of the triangle whose vertices are (a, b + c), (a, b – c) and (–a, c).
(a) 2ac
(b) 2bc
(c) b(a + c)
(d) c(a – b)
Answer :AShow Answer :
Question :. Find the area of the quadrilateral, the coordinates of whose angular points taken in order are (1, 1), (3, 4), (5, –2) and (4, –7).
(a) 20.5 sq. units
(b) 41 sq. units
(c) 82 sq. units
(d) 61.5 sq. units
Answer :AShow Answer :
Question : Four vertices of a parallelogram taken in order are (–3, –1), (a, b), (3, 3) and (4, 3). What will be the ratio of a and b?
(a) 4 : 1
(b) 1 : 2
(c) 1 : 3
(d) 3 : 1
Answer :AShow Answer :
Question : The points (1, 1), (–1, 5), (7, 9) and (9, 5) taken in such order that it will form a
(a) Rectangle
(b) Square
(c) Rhombus
(d) None of these
Answer :AShow Answer :
Question : In the given figure, PQRS is a straight lineR is the mid point of QS and Q is the midpoint of PS. S is (6, 5), R is (3, 5) and Tis (4, 8). Find the length of median TU.
(a) √13 units
(b) √50 units
(c) 2 √28 units
(d) √58 units
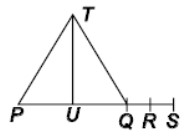
Answer 😀Show Answer :
Question : The name of the horizontal line in the cartesian plane which determines the position of a point is called:
(a) Origin
(b) X-axis
(c) Y-axis
(d) Quadrants
Answer : bShow Answer :
Question : The name of the vertical line in the cartesian plane which determines the position of a point is called:
(a) Origin
(b) X-axis
(c) Y-axis
(d) Quadrants
Answer : cShow Answer :
Question : The section formed by horizontal and vertical lines determining the position of the point in a cartesian plane is called:
(a) Origin
(b) X-axis
(c) Y-axis
(d) Quadrants
Answer : dShow Answer :
Question : The point of intersection of horizontal and vertical lines determining the position of a point in a cartesian plane is called:
(a) Origin
(b) X-axis
(c) Y-axis
(d) Quadrants
Answer : aShow Answer :
Question : If the coordinates of a point are (0, -4), then it lies in:
(a) X-axis
(b) Y-axis
(c) At origin
(d) Between x-axis and y-axis
Answer : bShow Answer :
Explanation: Since, x=0 and y=-4. Hence, the point will lie in the negative y-axis 4 units far from the origin.
Question : If the points (a, 0), (0, b) and (1, 1) are collinear then which of the following is true?
(a) 1/a + 1/b = 2
(b) 1/a – 1/b = 1
(c) 1/a – 1/b = 2
(d) 1/a + 1/b = 1
Answer 😀Show Answer :
Question : Three points A(1, –2), B(3, 4) and C(4, 7) form
(a) A straight line
(b) An equilateral triangle
(c) A right-angled triangle
(d) None of these
Answer :AShow Answer :
Question : In what ratio is the line segment joining the points (–3, 2) and (6, 1) is divided by Y-axis ?
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 2 : 1
(c) 1 : 2
(d) 3 : 1
Answer :CShow Answer :
Question : Find the coordinates of the point on X-axis which are equidistant from the points (–3, 4) and (2, 5).
(a) (20, 0)
(b) (–23, 0)
(c) (4/7X0)
(d) None of these
Answer 😀Show Answer :
Question : If the centroid of the triangle formed by the points (a, b), (b, c) and (c, a) is at the origin, then a3 + b3 + c3 =
(a) abc
(b) 0
(c) a + b + c
(d) 3 abc
Answer 😀Show Answer :
Question :Ayush starts walking from his house to office. Instead of going to the office directly, he goes to a bank first, from there to his daughter’s school and then reaches the office. If the house is situated at (2, 4), bank at (5, 8), school at (13, 14) and office at (13, 26) and coordinates are in km. What is the extra distance travelled by Ayushin reaching his office? (Assume that all distances covered are in straight lines)
(a) 2.2 km
(b) 2.7 km
(c) 11 √3km
(d) 2.40 km
Answer 😀Show Answer :
DIRECTION (17-18) : Students of a school are standing in rows and columns in their playground for drill practice. A, B, C and D are the position of the four students as shown in the figure.
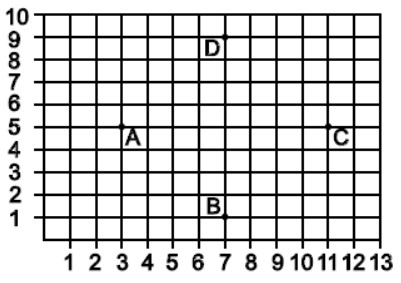
Question : What is the difference of distance between AC and AD ?
(a) 2 units
(b) 2.14 units
(c) 8 units
(d) 2.3 units
Answer 😀Show Answer :





